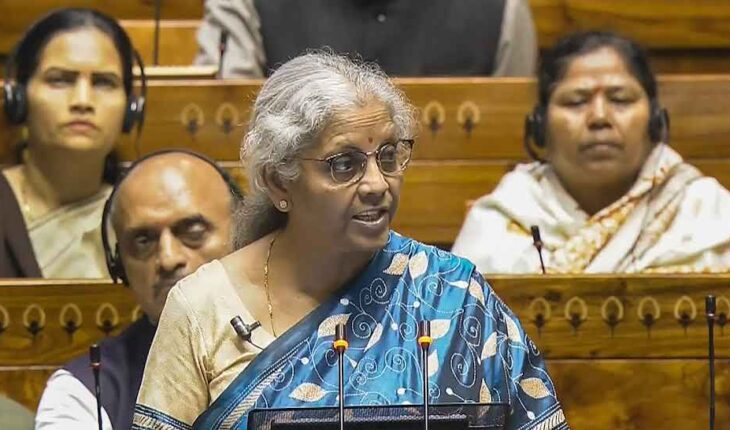
Recently, Hon’ble Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman presented the failures of the 10 years of the UPA government and the achievements of the 10 years of the Modi government through a white paper in the Lok Sabha. It has been said in this paper that before 2014, the country was facing economic crisis, due to which the Modi government had to work hard to bring the economy back on track. In response to this, Congress presented a black paper, in which it mentioned the failures of the Modi government and said that the BJP is working to end democracy and employment is not being created in the country during the tenure of Modi Government. Besides, inflation is also out of control.
Economic reforms started in 1991, but now work is being done rapidly in this direction. In 1991, many measures were taken to bring positive changes in the areas of foreign trade, tax reforms, foreign investment etc., which helped the Indian economy to progress. Before the Modi government came to power in 2014, India’s GDP at current prices was $1.8 trillion in 2013 and about $1 trillion in 2007. Thus, after exactly 60 years from 1947, India’s GDP reached $1 trillion in 2007 and increased to $2 trillion in 2014 and $3 trillion in 2019.
Today, in terms of real GDP, the Indian economy has become worth 3 trillion dollars. In 2014, the Indian economy became the tenth largest economy in the world, whereas in 2019, within just 5 years, it became the fifth largest economy in the world.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India’s GDP at current prices is currently $ 3.73 trillion, whereas when India became independent, its GDP was $ 227 billion. The USA’s GDP at current prices is $26.9 trillion and ranks first in the world, while China is at second place with a GDP of $17.8 trillion at current prices. In this order, Germany is at third place with GDP of 4.4 trillion dollars at current price and Japan is at fourth place with GDP of 4.2 trillion dollars at current price.
After coming to power, Modi government made many reforms in the banking and economic sector, the most important of which is the launch of Goods and Services Tax (GST), merger of banks, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, PM-Swanidhi Yojana, Launch of Atal Pension Yojana, Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana, Indian Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) etc.
In the report “The Indian Economy: A Review”, the journey of the last 10 years of the Modi government has been described as very important in terms of economic reforms. According to the report, nominal GDP is likely to grow at 7 percent in fiscal year 2025, while GDP is expected to grow at the rate of 7.3 percent in fiscal year 2024. Not only this, in this report it has also been predicted that India’s GDP can grow at the rate of 7 percent by 2030. Global rating agency S&P Global has also confirmed this claim of the government due to the strength of India’s financial sector and the recent structural reforms undertaken by the government.
S&P Global in its Global Credit Outlook 2024 report “New Risk, New Playbook” said India’s nominal GDP will grow from $3.5 trillion in 2022 to $7.3 trillion by 2030. There is no exaggeration in this estimate, because this target can be achieved with the GDP growth estimate at the rate of 6.3 percent, but according to the report of “The Indian Economy: A Review” and the report of S&P Global, the Indian economy can grow at a rate of more than 7 percent by 2030, whereas at present the annual pace of economic growth in USA is 1.58 percent, while that of China is 6.3 percent, that of Japan is 1.3 percent and that of Germany is 0.2 percent. In such a situation, the size of the Indian economy will reach 5 trillion dollars in 2027 and more than 7 trillion dollars in 2030.
The Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) scale is also used to measure the strength of a country’s economy. Under this concept, to compare the productivity and quality of human living between two countries, a comparison is made between the purchasing power of the currencies of two or more countries along with the services and products of those countries. If a person’s hair cutting is done for 170 rupees in India and 2 dollars in USA, then 170 rupees is equivalent to 2 dollars, that is, the price of the same service is the same in India and USA. This is called Purchasing Power Parity. In terms of PPP, India was the third largest economy in the world in 2023 with a GDP of $13.119 trillion, while China was at the first place in the world with a GDP of $30.3 trillion. At the same time, USA was in second place with a GDP of 25.4 trillion dollars.
For the first time in the eighties, the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) index crossed the 1000 points in the year FY 1989-90. In the year 2006, the BSE index crossed the 10,000 points. Then in the financial year 2014-15 it crossed the level of 30,000 points and in the financial year 2018-19, it crossed the level of 40,000 points, which crossed the record 70,000 points level in the year 2023. Nifty index also crossed the record level of 21,000 points in the year 2023.
Inflation and unemployment rates are under control in India. Also, per capita income is increasing steadily. On this basis, it can be assumed that the Indian economy will remain strong in the coming years also. Yes, the percentage of government debt as a proportion of GDP is high, but due to the increase in GST and other tax and non-tax revenue collections, this percentage may come down slightly in the coming years.
Satish Singh, Ahmedabad based Senior Columnist,Views are personal